Why Joomla Email Delivery Still Matters in 2026
Email is not just a communication tool; for Joomla websites, it is the lifeline of transactional functionality. Whether it’s user registration confirmations, password resets, or payment receipts, these messages are critical. A single misconfigured server can halt workflows, frustrate users, and damage trust.
But email setup inside of Joomla is difficult, and needs careful configuration. Email systems have grown into complex systems with multiple complex security configuration elements which all need to work correctly to enable proper email delivery. Spammers have made it impossible to allow simple connections to an email server to send messages with no real concerns.
Lets take a dive in to what needs to be set up to enable email to work smoothly.
TL:DR – Fortunately, if you use Google Workspace, theres a relatively easy solution to allowing Joomlas Server emails to be able to be sent - App Passwords!
Contents
- Why Joomla Email Delivery Still Matters in 2026
- Transactional emails as critical infrastructure, not a nice-to-have
- What breaks when server email is misconfigured
- The 2026 Reality Check: Google Workspace Email Changes
- Where Google has tightened security since the early 2020s
- The current status of “less secure apps” and why they’re gone for good
- What Google actually supports now (and what it quietly discourages)
- How Joomla Sends Email Under the Hood
- Joomla’s mailer options: PHP Mail, Sendmail, SMTP
- Why SMTP is still the only sensible choice
- Where Joomla’s configuration stops and your server’s responsibility begins
- Using Google Workspace SMTP with Joomla
- SMTP via smtp.gmail.com: what still works in 2026
- Ports, encryption, and authentication that won’t get blocked
- Performance and rate limits you need to design around
- App Passwords: Still Viable, Still Fragile
- When app passwords are allowed (and when they aren’t)
- Setting up an App Password in Google Workspace and using it with Joomla Mail settings
- Workspace account requirements and admin-level controls
- Risk profile of app passwords for production Joomla sites
- OAuth 2.0 with Joomla: Ideal in Theory, Awkward in Practice
- Why OAuth is Google’s preferred model
- The current state of Joomla extensions that support OAuth
- Operational complexity versus real-world benefit
- SMTP Relay as the Grown-Up Option
- Using Google Workspace SMTP relay with fixed IPs
- Authentication by IP, SPF, or both
- Why relay is often the cleanest setup for servers and clusters
- One Mailbox, Many Roles: Aliases Done Properly
- receipts@, payments@, no-reply@: what aliases are actually for
- How Google Workspace handles aliases at the SMTP level
- Mapping Joomla “From” addresses without breaking delivery
- The No-Reply Debate: Convenience vs Trust
- When no-reply addresses make sense
- Why Google and spam filters are increasingly sceptical
- Better patterns: monitored inboxes with auto-triage
- SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Non-Negotiable in 2026
- Why “email works” is no longer a valid test
- Correct SPF records for Google Workspace plus servers
- Enforcing DKIM and moving DMARC from monitor to policy
- Deliverability and Reputation Management
- How Google judges your Joomla-generated email
- Warming up domains and IPs after changes
- Common Joomla patterns that trigger spam scoring
- Security Hardening for Joomla Email
- Limiting credentials exposure on shared hosting and VPSs
- Environment variables, config.php, and secrets hygiene
- What to do when credentials leak (because eventually they will)
- Testing and Monitoring Email the Right Way
- Why sending yourself a test email is meaningless
- Tools and headers that actually show delivery health
- Logging and alerting before users complain
- Common Failure Modes and How to Fix Them
- Emails send but never arrive
- Emails land in spam after “working for years”
- Google blocks the account without warning
- Future-Proofing Beyond Google Workspace
- When it’s time to stop using Workspace for server email
- Transactional email services as a pressure release valve
- Designing Joomla setups that can swap providers cleanly
- Practical Configuration Checklist for 2026
- Minimum viable secure setup
- Recommended production-grade setup
- Red flags that mean you should rethink the architecture
Transactional emails as critical infrastructure, not a nice-to-have
Transactional emails underpin operations. Unlike marketing campaigns, they are expected, immediate, and legally significant. Receipts, invoices, or account notifications rely on timely delivery. Without them, operations grind to a halt.
What breaks when server email is misconfigured
Misconfigured email servers result in undelivered confirmations, abandoned registrations, and lost payment notifications. Spam filters may flag legitimate emails, domains can get blacklisted, and support tickets surge. The reputation of the website suffers almost instantly.
The 2026 Reality Check: Google Workspace Email Changes
Where Google has tightened security since the early 2020s
Google has significantly increased anti-abuse measures. Security defaults now prevent unauthenticated applications from sending email. Servers that do not adhere to modern authentication protocols are increasingly blocked. Legacy access methods are no longer viable.
The current status of “less secure apps” and why they’re gone for good
“Less secure apps” are obsolete. Google removed this option to prevent credential theft and phishing. Joomla websites relying on old PHP Mail or simple SMTP authentication without encryption will fail to send messages reliably.
What Google actually supports now (and what it quietly discourages)
Google fully supports OAuth 2.0, SMTP relay, and app passwords with constraints. Direct username/password SMTP login is discouraged and often blocked. Configurations ignoring SPF, DKIM, or DMARC are flagged or rejected silently.
How Joomla Sends Email Under the Hood
Joomla’s mailer options: PHP Mail, Sendmail, SMTP
Joomla provides three main options: PHP Mail, Sendmail, and SMTP. PHP Mail is simple but unreliable. Sendmail is server-dependent and often inconsistent. SMTP offers control, authentication, and secure delivery.
Why SMTP is still the only sensible choice
SMTP ensures encrypted transmission, accountability, and proper authentication. It works with Google Workspace reliably and integrates with modern spam-prevention measures. PHP Mail is increasingly fragile, hard to set up and can be flagged as spam due to unauthenticated sending.
Where Joomla’s configuration stops and your server’s responsibility begins
Joomla can configure SMTP details, but the server must allow outbound connections, proper DNS records, and IP reputation management. Without server-side compliance, emails will fail even if Joomla is configured correctly. This is one of the reasons it is complicated. There are many moving parts and debugging is difficult.
Using Google Workspace SMTP with Joomla
SMTP via smtp.gmail.com: what still works in 2026
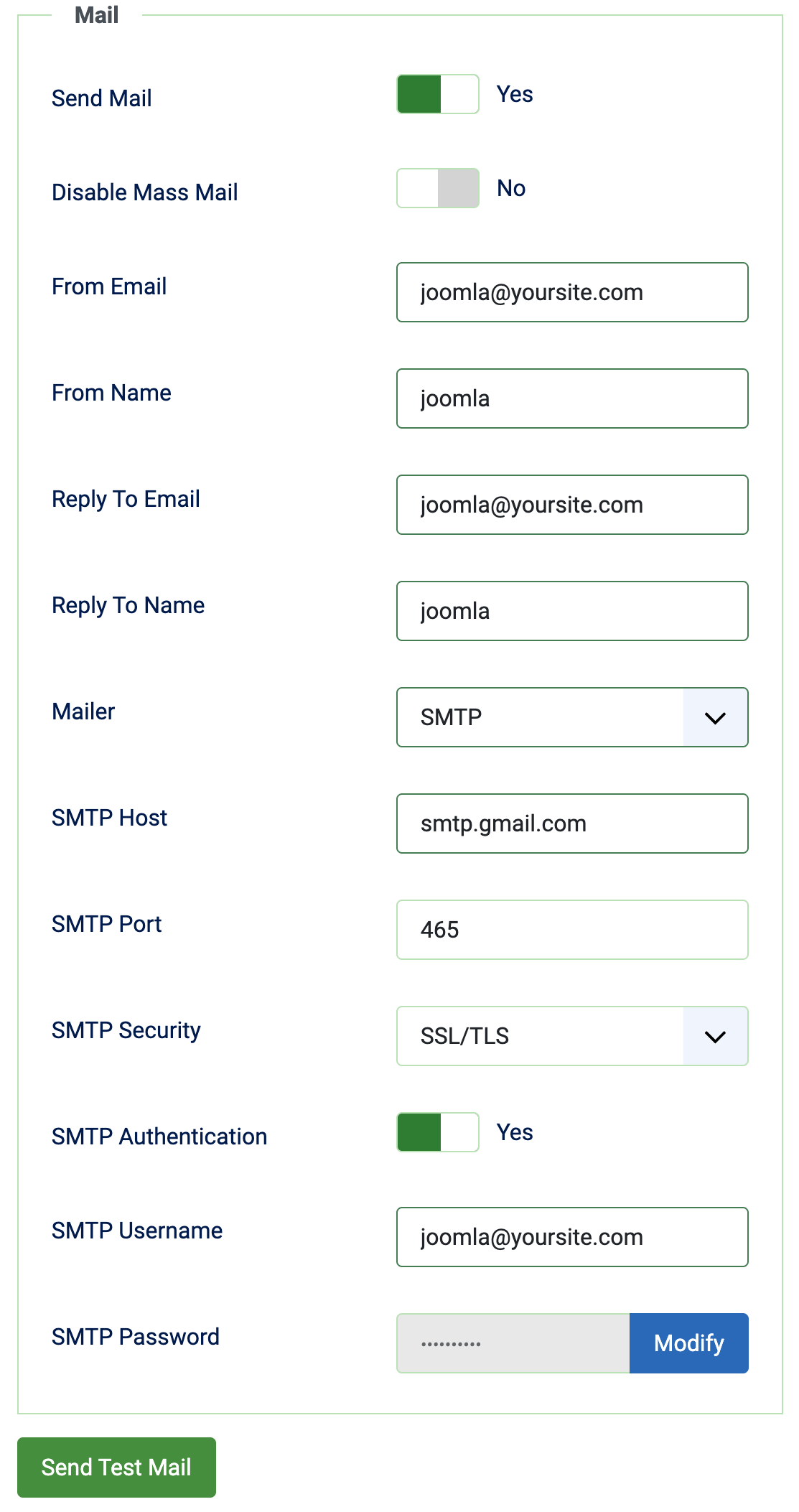
The primary endpoint remains smtp.gmail.com with SSL/TLS encryption. Authentication must use OAuth or an approved app password with a multi-factor enabled account. Plain password SMTP is blocked these days. Joomla's built in mail settings don't support OAuth.
Ports, encryption, and authentication that won’t get blocked
Port 465 with SSL and port 587 with STARTTLS remain supported. Encryption is mandatory. Authentication requires either OAuth tokens or an app password with a multi-factor enabled accounts.
Performance and rate limits you need to design around
Google enforces strict limits: per-account sending quotas, per-minute limits, and batch restrictions. High-volume Joomla sites wound need to hink about using extensions that queue emails or implement batching to avoid throttling or account suspension.
App Passwords: Still Viable, Still Fragile
When app passwords are allowed (and when they aren’t)
App passwords are only allowed for accounts with two-factor authentication enabled. They are blocked for accounts managed by certain enterprise policies or disabled by administrators. They offer a good workable solution when you cannot use "Sign in with Google.", but if the end user password is changed the app password is invalidated so they require monitoring if this happens.
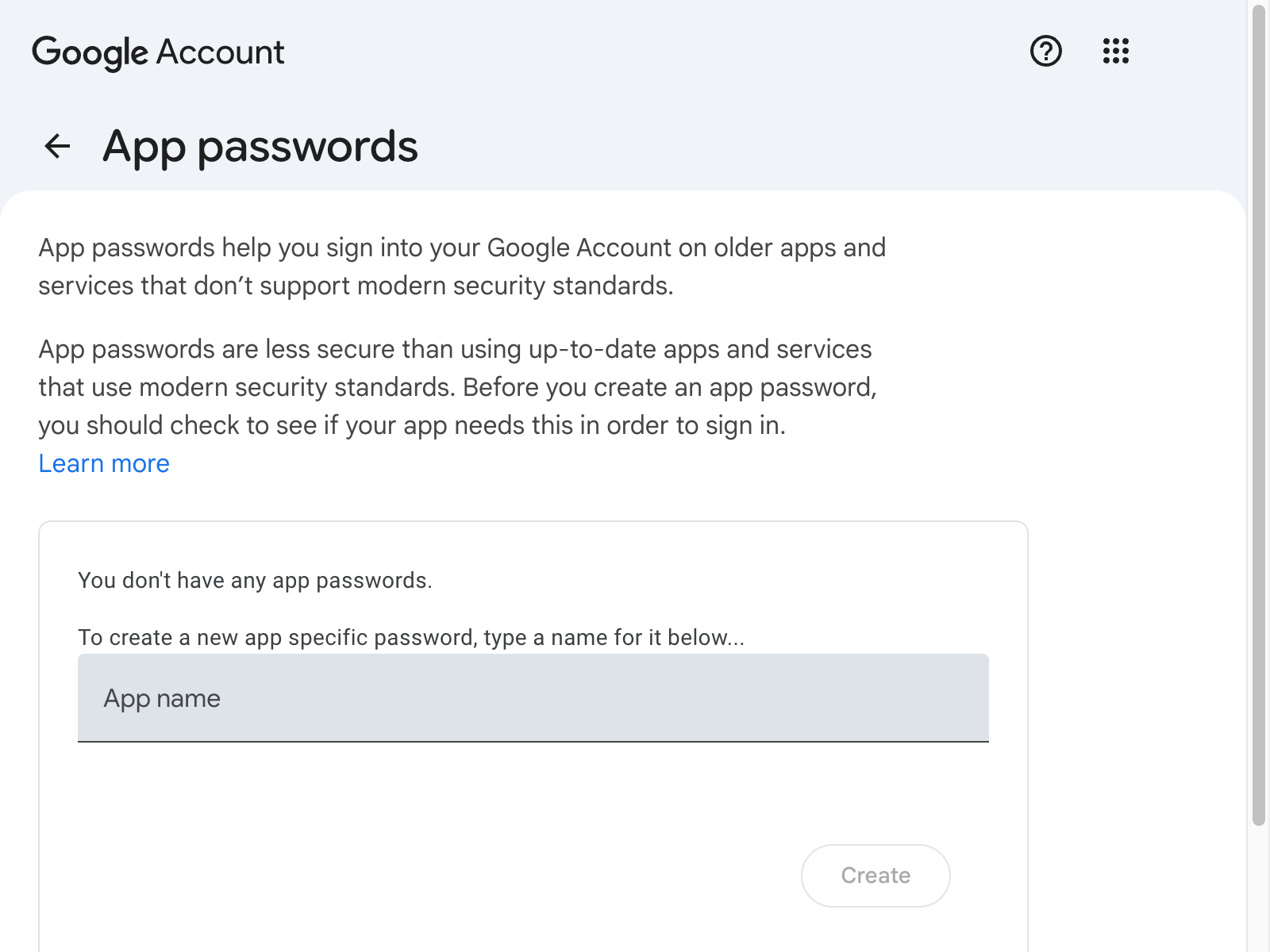
Setting up an App Password in Google Workspace and using it with Joomla Mail settings
It is best to create an email account specifically for this purpose if you can to separate these emails from ordinary user emails and reduce the password change invalidated the app password fragility of this approach.
- You'll need to enable two-factor authentication.
- Then navigate to Create and manage app passwords while in a browser signed in to the Google Account for which you wish to have an App password.
- You can use the generated password in the SMTP password field, with that email account as the email account name.
- You'll need to change the app password if the email account password changes.
- Click Send Test Email and check the joomla message and the email account for your test message.
- If you completed this successfully your Joomla system is now able to send emails!
Workspace account requirements and admin-level controls
Admins can enforce or restrict app password usage across the domain. Permissions and organisational units determine who can generate passwords. Proper policies prevent accidental exposure of credentials.
Risk profile of app passwords for production Joomla sites
App passwords bypass two-factor authentication, so if leaked, they compromise the account. For production sites, rotate credentials regularly and limit permissions. Monitoring is essential to avoid abuse.
OAuth 2.0 with Joomla: Ideal in Theory, Awkward in Practice
Why OAuth is Google’s preferred model
OAuth 2.0 provides token-based authentication, removes direct password storage, and integrates cleanly with modern security requirements. It is future-proof and compliant with Google’s roadmap.
The current state of Joomla extensions that support OAuth
Few Joomla extensions fully implement OAuth 2.0 and Joomlas Server email settings do not support it. Extensions supporting OAuth are more complex to configure but offer would offer stronger long-term security. There is a good case for modernising the Joomla Server email settings to support OAuth. Perhaps someone will take it on. The challenge would be making it vendor agnostic enought for the Joomla Core. There are some exentions which support OAuth but they don't seem to offer the simplicity of the current settings and often require exensive configuration at the backend - in this case Google Cloud or Google Workplace.
Operational complexity versus real-world benefit
OAuth improves security but adds token management, renewals, and possible downtime if misconfigured. Smaller sites often opt for controlled app passwords for simplicity, accepting the trade-off.
SMTP Relay as the Grown-Up Option
Using Google Workspace SMTP relay with fixed IPs
For organisations with fixed server IPs, SMTP relay allows sending without passwords. Only approved IPs can relay messages, reducing the risk of credential leakage and improving deliverability.Some Google Workspace plans (including the original free legacy Google Apps for your Domain plans) do not support using SMTP relay.
Authentication by IP, SPF, or both
Combine IP whitelisting with SPF records for domain authentication. DKIM signatures further validate the origin. This layered approach is recommended for production reliability.
Why relay is often the cleanest setup for servers and clusters
SMTP relay decouples Joomla from credentials, supports multiple servers sending as the same domain, and ensures compliance with Google’s security policies. It scales better than app-password-based SMTP.
One Mailbox, Many Roles: Aliases Done Properly
receipts@, payments@, no-reply@: what aliases are actually for
Aliases allow one mailbox to handle multiple functions without creating separate accounts. Receipts@ and payments@ manage transactional flows. no-reply@ signals automated messages, though it must be used judiciously.
How Google Workspace handles aliases at the SMTP level
Google allows sending as an alias from a single account. Proper configuration in Gmail and Joomla ensures “From” addresses match verified aliases. Misalignment triggers SPF or DMARC warnings.
Mapping Joomla “From” addresses without breaking delivery
Configure each Joomla mailer instance with the verified alias. Avoid dynamically changing “From” to unverified addresses. Maintain consistent sender identity to prevent spam scoring.
The No-Reply Debate: Convenience vs Trust
When no-reply addresses make sense
No-reply is useful for notifications that do not require user replies, such as system logs or automated receipts. It communicates that the mailbox is not monitored.
Why Google and spam filters are increasingly sceptical
No-reply addresses can appear suspicious. Spam filters associate them with unmonitored accounts and phishing attempts. Overuse can reduce deliverability and user trust.
Better patterns: monitored inboxes with auto-triage
Use a monitored inbox with automated filters. Replies can be acknowledged or forwarded. This approach balances convenience, user experience, and deliverability.
SPF, DKIM, and DMARC: Non-Negotiable in 2026
Why “email works” is no longer a valid test
Sending an email successfully from Joomla does not guarantee delivery. ISPs check authentication records, sender reputation, and domain alignment. Without SPF, DKIM, and DMARC, messages are flagged or discarded.
Correct SPF records for Google Workspace plus servers
SPF should include Google Workspace and all server IPs authorised to send. Syntax must be precise. Overly broad or incorrect records reduce trustworthiness.
Enforcing DKIM and moving DMARC from monitor to policy
DKIM signing ensures message integrity. DMARC policies enforce rejection or quarantine of unauthenticated messages. Monitoring only is insufficient in 2026; enforcement is required for reliable delivery.
Deliverability and Reputation Management
How Google judges your Joomla-generated email
Google evaluates SPF/DKIM alignment, IP reputation, content patterns, and user interaction. Frequent bounces or spam complaints reduce deliverability, even if technical settings are correct.
Warming up domains and IPs after changes
New domains or IPs should send gradually increasing volumes. Sudden spikes trigger spam filters. Proper warming protects long-term reputation.
Common Joomla patterns that trigger spam scoring
Mass identical subjects, inconsistent “From” addresses, and excessive links or HTML can trigger spam filters. Review templates and automate quality checks before sending.
Security Hardening for Joomla Email
Limiting credentials exposure on shared hosting and VPSs
Do not store SMTP passwords in web-accessible directories. Use environment variables or protected configuration files. Restrict file permissions rigorously.
Environment variables, config.php, and secrets hygiene
config.php should never contain plaintext passwords accessible to the public. Environment variables or encrypted storage is preferred. Rotate secrets regularly.
What to do when credentials leak (because eventually they will)
Immediately revoke the compromised password or app token. Review logs for abuse. Rotate all related credentials and update Joomla configuration.
Testing and Monitoring Email the Right Way
Why sending yourself a test email is meaningless
A single test does not reveal deliverability issues. Emails might reach your inbox but fail for other domains or trigger spam filters elsewhere.
Tools and headers that actually show delivery health
Examine SPF, DKIM, DMARC headers, and bounce reports. Use third-party monitoring services or command-line tools to validate deliverability across ISPs.
Logging and alerting before users complain
Maintain detailed logs of all outgoing messages. Alert on failed deliveries, bounces, or Google blocks. Proactive monitoring prevents service disruption and user complaints.
Common Failure Modes and How to Fix Them
Emails send but never arrive
Check SPF/DKIM alignment, IP reputation, and content. Verify SMTP configuration and relay settings. Often misalignment or misconfigured relays are the cause.
Emails land in spam after “working for years”
Reputation decay, new filtering algorithms, or outdated SPF/DKIM records cause this. Revalidate all authentication settings and monitor user complaints.
Google blocks the account without warning
Sudden spikes, suspicious activity, or outdated credentials trigger blocks. Implement monitoring, rate-limiting, and alternate authentication to mitigate.
Future-Proofing Beyond Google Workspace
When it’s time to stop using Workspace for server email
If volume, reliability, or security demands exceed Workspace limits, consider specialised transactional email services. High-volume Joomla sites may outgrow Google Workspace SMTP.
Transactional email services as a pressure release valve
Services like SendGrid, Mailgun, or Amazon SES offer better monitoring, scalability, and delivery guarantees. They integrate with Joomla via SMTP or APIs.
Designing Joomla setups that can swap providers cleanly
Abstract SMTP settings in Joomla configuration, avoid hardcoding credentials, and test multiple endpoints. This ensures smooth migration without downtime.
Practical Configuration Checklist for 2026
Minimum viable secure setup
Joomla configured with SMTP, verified Google Workspace alias, SPF/DKIM records in place, app password or relay enabled, basic logging active.
Recommended production-grade setup
OAuth 2.0 or SMTP relay, strict SPF/DKIM/DMARC enforcement, monitored inboxes, domain/IP warming, logging with alerts, IP whitelisting, automated templates checked for spam triggers.
Red flags that mean you should rethink the architecture
Emails frequently land in spam, repeated Google blocks, lack of monitoring, multiple Joomla servers sending unauthenticated email, or credentials stored insecurely. Address these before scaling operations.

